Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections that can occur in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs are caused by bacteria, but can also be caused by viruses or fungi. UTIs are more common in women than in men due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder. The most common type of UTI is a bladder infection, which occurs when bacteria enter the bladder and cause inflammation.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. UTIs are caused by bacteria, and common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate, even if only small amounts of urine are produced
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
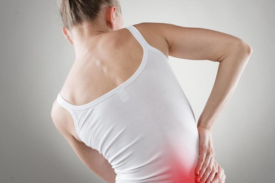
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
- Fever or chills (which may indicate a more serious infection affecting the kidneys)
In older adults, especially those over 65, symptoms of a UTI may be more vague and nonspecific. They may include:
- Confusion or delirium
- Weakness or fatigue
- Loss of appetite or nausea
- Incontinence
- Falling or balance problems
- Fever or chills
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. UTIs can usually be treated with antibiotics, but untreated infections can lead to more serious health problems, especially in older adults or those with weakened immune systems.
Causes of UTI
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are more common in women than in men, in part due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder. Some common causes of UTIs in women include:
- Sexual activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra and increase the risk of UTIs. This is commonly referred to as “honeymoon cystitis” because it is more likely to occur after sexual activity.
- Poor hygiene: Wiping from back to front after using the toilet can introduce bacteria from the anal area into the urethra, increasing the risk of UTIs.
- Contraceptive use: Women who use certain types of contraceptives, such as diaphragms or spermicidal agents, may have an increased risk of UTIs.
- Menopause: Changes in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to changes in the urinary tract that increase the risk of UTIs.
- Pregnancy: Changes in the urinary tract during pregnancy, as well as increased pressure on the bladder, can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system, can increase the risk of UTIs.
It is important for women to practice good hygiene and seek medical attention if they experience symptoms of a UTI, as untreated infections can lead to more serious complications. UTIs can usually be treated with antibiotics, but in some cases, further evaluation may be needed to identify and manage underlying risk factors.
Prevention of UTIs in Women:
There are several ways that women can help prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs):
- Practice good hygiene: Wiping from front to back after using the toilet can help prevent the spread of bacteria from the anal area to the urethra.
- Urinate after sex: Urinating after sexual activity can help flush out bacteria that may have been introduced into the urinary tract during sex.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help flush out bacteria and reduce the risk of UTIs.
- Avoid irritating products: Using irritating products like douches, powders, or soaps in the genital area can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and increase the risk of UTIs.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing and breathable fabrics can help reduce moisture and prevent the growth of bacteria.
- Take showers instead of baths: Taking showers instead of baths can help reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Cranberry products: Some studies suggest that cranberry products, such as juice or supplements, may help prevent UTIs by reducing the ability of bacteria to adhere to the urinary tract lining.
It is important to note that while these measures can help reduce the risk of UTIs, they may not prevent all infections. If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it is important to seek medical attention and follow your healthcare provider’s recommended treatment plan.
Treatment of UTIs in Women:
The treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women usually involves a course of antibiotics to clear the infection. The specific type of antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the individual’s health history. Your healthcare provider may also recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to help manage symptoms like pain or discomfort during urination.
It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Failure to complete the course of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance and make future UTIs more difficult to treat.
For women who experience frequent UTIs, your healthcare provider may recommend further testing and evaluation to identify underlying risk factors or contributing factors, such as anatomical abnormalities, diabetes, or kidney stones. In some cases, prophylactic antibiotics may be recommended to prevent future infections.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of a UTI, as untreated infections can lead to more serious complications like kidney infections. It is also important to follow any instructions or recommendations provided by your healthcare provider to help prevent future infections.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue, particularly in women. These infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and can cause symptoms like pain or discomfort during urination, frequent urination, or cloudy urine. While UTIs can be uncomfortable, they are typically treatable with a course of antibiotics.
If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications. At https://www.puneurologist.in/ we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of UTIs and other urological conditions. Our team of experienced healthcare professionals provides comprehensive care to help you manage your symptoms and prevent future infections.
To reduce the risk of UTIs, it is important to practice good hygiene, stay hydrated, and avoid irritating products in the genital area. For women who experience recurrent UTIs, further evaluation may be necessary to identify underlying risk factors or contributing factors. With proper care and management, UTIs can be effectively treated and prevented.